List of diplomatic missions of Israel
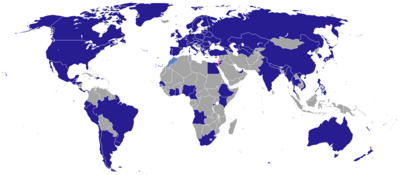
This is a list of diplomatic missions of Israel, excluding honorary consulates. As of November 2021, there are 82 resident embassies, including a Taiwan office, and 22 consulate-generals and two representative missions in the 165 states that recognise Israel.[1]
Israel also maintains five missions to multilateral organisations, of which four missions are to the United Nations and one mission to the European Union. Israel also maintains an economic and cultural office in Taiwan and a representative office to the International Renewable Energy Agency in the United Arab Emirates.[2]
Israel's biggest diplomatic coup in the international community came with peace treaties and recognition from Arab countries such as Egypt in the late 1970s, and Jordan in the early 1990s, leading to embassies being opened in Cairo and Amman. During the late 1980s, several Israeli embassies were opened/reopened in former Eastern Bloc states as the Cold War ended. At the beginning of the 1990s, Israel established official relations with the Soviet Union, India and China. The prospects of a Middle East peace agreement in the mid-1990s led to Israeli government offices appearing as trade representative offices being opened in a handful of Arab states such as Bahrain, Qatar, Tunisia, Oman and Morocco. By 2000s, all have since closed the Israeli offices.[3][4][5][6] Israel closed its embassies in Mauritania and Venezuela after the 2008 Gaza War, following a request to do so by their national governments. Following the signing of the Abraham Accords, Israel opened embassies in Abu Dhabi[7] and Manama in 2021,[8][9] a consulate-general in Dubai,[10] and a liaison office in Rabat.[11]
Africa[edit]
 Angola
Angola
- Luanda (Embassy)
 Cameroon
Cameroon
- Yaoundé (Embassy)
 Egypt
Egypt
- Cairo (Embassy)
 Ethiopia
Ethiopia
- Addis Ababa (Embassy)
 Ghana
Ghana
- Accra (Embassy)
 Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast
- Abidjan (Embassy)
 Kenya
Kenya
- Nairobi (Embassy)
 Morocco
Morocco
- Rabat (Liaison Office)
 Nigeria
Nigeria
- Abuja (Embassy)
 Rwanda
Rwanda
- Kigali (Embassy)
 Senegal
Senegal
- Dakar (Embassy)
 South Africa
South Africa
- Pretoria (Embassy)
Americas[edit]
 Argentina
Argentina
- Buenos Aires (Embassy)
 Brazil
Brazil
.svg/23px-Flag_of_Canada_(Pantone).svg.png) Canada
Canada
 Chile
Chile
- Santiago de Chile (Embassy)
 Costa Rica
Costa Rica
- San José (Embassy)
 Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic
- Santo Domingo (Embassy)
 Ecuador
Ecuador
- Quito (Embassy)
 Guatemala
Guatemala
- Guatemala City (Embassy)
 Honduras
Honduras
- Tegucigalpa (Embassy)
 Mexico
Mexico
- Mexico City (Embassy)
 Panama
Panama
- Panama City (Embassy)
 Peru
Peru
- Lima (Embassy)
.png/23px-Flag_of_the_United_States_(23px).png) United States
United States
- Washington, D.C. (Embassy)
- Atlanta (Consulate-General)
- Boston (Consulate-General)
- Chicago (Consulate-General)
- Houston (Consulate-General)
- Los Angeles (Consulate-General)
- Miami (Consulate-General)
- New York (Consulate-General)
- San Francisco (Consulate-General)
 Uruguay
Uruguay
- Montevideo (Embassy)
Asia[edit]
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
- Baku (Embassy)
 Bahrain
Bahrain
- Manama (Embassy)
 China
China
 Georgia
Georgia
- Tbilisi (Embassy)
 India
India
 Japan
Japan
- Tokyo (Embassy)
 Jordan
Jordan
- Amman (Embassy)
 Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan
- Astana (Embassy)
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Nepal
Nepal
 Philippines
Philippines
 Singapore
Singapore
- Singapore (Embassy)
 South Korea
South Korea
- Seoul (Embassy)
 Taiwan
Taiwan
- Taipei (Israel Economic and Cultural Office in Taipei)
 Thailand
Thailand
- Bangkok (Embassy)
 Turkey
Turkey
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
- Ashgabat (Embassy)
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
- Tashkent (Embassy)
 Vietnam
Vietnam
- Hanoi (Embassy)
Europe[edit]
 Albania
Albania
- Tirana (Embassy)
 Austria
Austria
- Vienna (Embassy)
 Belarus
Belarus
- Minsk (Embassy)
.svg/23px-Flag_of_Belgium_(civil).svg.png) Belgium
Belgium
- Brussels (Embassy)
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
- Sofia (Embassy)
 Croatia
Croatia
- Zagreb (Embassy)
 Cyprus
Cyprus
- Nicosia (Embassy)
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
- Prague (Embassy)
 Denmark
Denmark
- Copenhagen (Embassy)
 Finland
Finland
- Helsinki (Embassy)
 France
France
 Germany
Germany
 Greece
Greece
.svg/15px-Flag_of_the_Vatican_City_(2001–2023).svg.png) Holy See
Holy See
 Hungary
Hungary
- Budapest (Embassy)
 Ireland
Ireland
- Dublin (Embassy)
 Italy
Italy
- Rome (Embassy)
 Kosovo
Kosovo
 Latvia
Latvia
- Riga (Embassy)
 Lithuania
Lithuania
- Vilnius (Embassy)
 Netherlands
Netherlands
- The Hague (Embassy)
 Norway
Norway
- Oslo (Embassy)
 Poland
Poland
- Warsaw (Embassy)
 Portugal
Portugal
- Lisbon (Embassy)
 Romania
Romania
- Bucharest (Embassy)
 Russia
Russia
- Moscow (Embassy)
- St. Petersburg (Consulate-General)
 Serbia
Serbia
- Belgrade (Embassy)
 Slovakia
Slovakia
- Bratislava (Embassy)
 Spain
Spain
- Madrid (Embassy)
 Sweden
Sweden
- Stockholm (Embassy)
.svg/16px-Flag_of_Switzerland_(Pantone).svg.png) Switzerland
Switzerland
- Bern (Embassy)
 Ukraine
Ukraine
- Kyiv (Embassy)
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
Oceania[edit]
.svg/23px-Flag_of_Australia_(converted).svg.png) Australia
Australia
- Canberra (Embassy)
 New Zealand
New Zealand
- Wellington (Embassy)
Multilateral organisations[edit]
- Brussels (permanent mission to the European Union)
- Geneva (permanent mission to United Nations institutions)
- New York City (permanent mission to the United Nations)
- Paris (permanent mission to United Nations institutions)
- Vienna (permanent mission to United Nations institutions)
Gallery[edit]
-
Embassy in Athens
-
Embassy in Beijing
-
Embassy in Berlin
-
Embassy in Brasília
-
Embassy in Canberra
-
Embassy in Dublin
-
Embassy in The Hague
-
Embassy in Helsinki
-
Embassy in Kyiv
-
Embassy in Lima
-
Embassy in Oslo
-
Embassy in Paris
-
Embassy in Prague
-
Embassy in Stockholm
-
Embassy in Tokyo
-
Embassy in Warsaw
Diplomatic missions to open[edit]
 Armenia
Armenia
 Chad
Chad
- N'Djamena (Embassy)
 Democratic Republic of the Congo
Democratic Republic of the Congo
 Morocco
Morocco
 Paraguay
Paraguay
 Sudan
Sudan
- Khartoum (Embassy)
Closed missions[edit]
.svg/23px-Flag_of_Australia_(converted).svg.png) Australia
Australia
- Sydney (Consulate-General) — opened in 1949, closed in 2002
 Benin
Benin
- Cotonou (Embassy) — opened in 1964, closed in 1973
.svg/22px-Bandera_de_Bolivia_(Estado).svg.png) Bolivia
Bolivia
- La Paz (Embassy) — opened in 1975, closed in 2009
 Brazil
Brazil
- Rio de Janeiro (Consulate-General) — opened in 1949, closed in 2002
 Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso
- Ouagadougou (Embassy) — opened in 1964, closed in 1973
 Cambodia
Cambodia
- Phnom Penh (Embassy) — opened in 1967, closed in 1975
 Central African Republic
Central African Republic
- Bangui (Embassy) — opened in 1961, closed in 1973
 Colombia
Colombia
- Bogota (Embassy) — opened in 1957, closed in 2024
 Republic of the Congo
Republic of the Congo
- Brazzaville (Embassy) — opened in 1960, closed in 1972
 Cuba
Cuba
- Havana (Embassy) — opened in 1960, closed in 1973
 Democratic Republic of the Congo
Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Kinshasa (Embassy) — opened in 1982, closed in 2003
 Egypt
Egypt
- Alexandria (Consulate-General) — opened in 1982, closed in 2002
 El Salvador
El Salvador
- San Salvador (Embassy) — opened in 1974, closed in 2016
 Eritrea
Eritrea
- Asmara (Embassy) — opened in 1993, closed in 2022
 Eswatini
Eswatini
- Mbabane (Embassy) — opened in 1968, closed in 1996
 Fiji
Fiji
- Suva (Embassy) — opened in 1987, closed in 1995
 France
France
- Marseille (Consulate-General) — opened in 1951, closed in 2015
 Gabon
Gabon
- Libreville (Embassy) — opened in 1963, closed in 1973
 Germany
Germany
- Bonn (Consulate-General) — opened in 1955, closed in 1967
 Guinea
Guinea
- Conakry (Embassy) — opened in 1959, closed in 1967
 Haiti
Haiti
- Port-au-Prince (Embassy) — opened in 1973, closed in 1990
 Iran
Iran
- Tehran (Embassy) — opened in 1964, closed in 1979
 Italy
Italy
- Milan (Consulate-General) — opened in 1967, closed in 1996
 Jamaica
Jamaica
- Kingston (Embassy) — opened in 1975, closed in 1995
 Lebanon
Lebanon
- Beirut (Representative Office) — opened in 1982, closed in 1984
 Liberia
Liberia
- Monrovia (Embassy) — opened in 1957, closed in 1973
 Madagascar
Madagascar
- Antananarivo (Embassy) — opened in 1960, closed in 1973
 Malawi
Malawi
- Lilongwe (Embassy) — opened in 1964, closed in 1997
 Mali
Mali
- Bamako (Embassy) — opened in 1960, closed in 1972
 Mauritania
Mauritania
- Nouakchott (Embassy) — opened in 1999, closed in 2009[18][19][20]
 Netherlands
Netherlands
- Amsterdam (Embassy) — opened in 1949, closed in 1970
 Niger
Niger
- Niamey (Embassy) — opened in 1961, closed in 1972
 Nigeria
Nigeria
- Lagos (Embassy) — opened in 1960, closed in 1973
 Oman
Oman
- Muscat (Commercial Office) — opened in 1996, closed in 2000
 Paraguay
Paraguay
- Asunción (Embassy) — opened in 2015, closed in 2018
 Qatar
Qatar
 Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone
- Freetown (Embassy) — opened in 1961, closed in 1973
 South Africa
South Africa
- Johannesburg (Embassy) — opened in 1949, closed in 1980
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
- Colombo (Interests Section) — opened in 1983, closed in 1990
.svg/16px-Flag_of_Switzerland_(Pantone).svg.png) Switzerland
Switzerland
- Zürich (Consulate-General) — opened in 1949, closed in 1990
 Tanzania
Tanzania
- Dar es Salaam (Embassy) — opened in 1961, closed in 1973
 Togo
Togo
- Lomé (Embassy) — opened in 1962, closed in 1973
 Tunisia
Tunisia
- Tunis (Representative Office) — opened in 1996, closed in 2000
 Uganda
Uganda
- Kampala (Embassy) — opened in 1962, closed in 1972
 United States
United States
- Dallas (Consulate-General) — opened in 1960, closed in 1962
- Philadelphia (Consulate-General) — opened in 1964, closed in 2015
 Venezuela
Venezuela
- Caracas (Embassy) — opened in 1958, closed in 2009
 Zambia
Zambia
- Lusaka (Embassy) — opened in 1964, closed in 1973
See also[edit]
Notes[edit]
- ^ The Israeli Embassy to the Holy See is located outside Vatican territory in Rome
References[edit]
- ^ embassies.gov.il : Israeli Missions Around The World
- ^ Israeli Delegation Discusses Cooperation with IRENA on Advancement of Renewable Energy
- ^ Gedalyahu, Tzvi Ben (27 June 2010). "Bahrain Red-Faced for 'Kissing Camel' Toy with Name 'Israel'". Arutz Sheva. Retrieved 2011-10-16. "Bahrain does not recognize Israel as a state, but Israel maintained a diplomatic mission in Bahrain before it was closed in 2000 at the start of the Second Intifada."
- ^ The Middle East: Abstracts and index. Library Information and Research Service. 1999. Retrieved 5 August 2011.
Tunisia and Israel announced on 10/3/1994 the establishment of low-level diplomatic relations, a move that both countries described as the first step in the normalization of ties. The two countries will establish economic liaison.
- ^ "Israel and Morocco: A Special Relationship" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 September 2011. Retrieved 5 August 2011.
- ^ "Oman recognizes Israel as a state". Retrieved 27 October 2018.
- ^ "Israel opens embassy in Abu Dhabi". Reuters. 24 January 2021. Retrieved 25 January 2021.
- ^ "Israeli Foreign Minister to Open New Bahrain Embassy on Thursday". Bloomberg. 29 September 2021. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ "Lapid inaugurates Israeli embassy in Bahrain". Times of Israel. 30 September 2021. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ "Lapid inaugurates Israeli Consulate in Dubai: 'We created the incredible'". The Jerusalem Post | JPost.com. Retrieved 2022-08-04.
- ^ "Israel's envoy inaugurates diplomatic mission in Morocco". AP NEWS. 2021-08-12. Retrieved 2022-08-04.
- ^ Kosovo’s president welcomes 1st-ever Israeli ambassador
- ^ "Armenian government approves bill to open Embassy in Israel". armenpress.am. Retrieved 2021-08-25.
- ^ Berman, Lazar; Staff, ToI. "DR Congo will move its embassy to Jerusalem, leader tells Netanyahu at UN sidelines". www.timesofisrael.com. Retrieved 2023-09-22.
- ^ "'Historic': Israel, Morocco agree on diplomatic ties 'as soon as possible'". The Times of Israel.
- ^ Rabat, Basma El Atti ــ (2023-02-27). "Israel starts construction work of new embassy in Rabat". www.newarab.com. Retrieved 2023-09-22.
- ^ "Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu to Paraguayan President Santiago Peña: "The most important thing we're going to do right away is to reopen the Paraguayan Embassy in Jerusalem and to reopen the Israeli Embassy in Asuncion."". GOV.IL. Retrieved 2023-09-22.
- ^ Sidi Salem, Hachem (6 March 2009). "Staff leave Israeli embassy in Mauritania". Thomson Reuters. Archived from the original on 2009-03-13. Retrieved 2022-06-13.
- ^ "Israel closes Mauritania embassy". BBC. 2009-03-06. Retrieved 2022-06-13.
- ^ Sidi Salem, Hachem; Fertey, Vincent (6 March 2009). "Mauritania expels Israeli diplomats, shuts embassy". Thomson Reuters. Archived from the original on 2021-06-06. Retrieved 2022-06-13.
- ^ "Qatar, Under Pressure, Will Close Israeli Trade Office". Los Angeles Times. 2000-11-10. Retrieved 2023-06-14.
- ^ "Qatar Closes Israel Trade Office Over Gaza Op, Expels Staff From Country". Haaretz. Retrieved 2023-06-14.
- ^ "Qatar closes Israeli trade office". Hindustan Times. 2009-01-19. Retrieved 2023-06-14.
- ^ "i24NEWS". www.i24news.tv. Retrieved 2023-06-14.
- ^ "Israel to close diplomatic office in Qatar with end of World Cup". Retrieved 2023-06-14.








.jpg/101px-Yrjönkatu_36_(Embassy_of_Israel_in_Helsinki).jpg)





_-_2021-08-23_-_2.jpg/150px-Rue_Rabelais_-_Paris_VIII_(FR75)_-_2021-08-23_-_2.jpg)





